This document shows some examples of embodied activities from our courses.
Embodied Activity: RNN¶
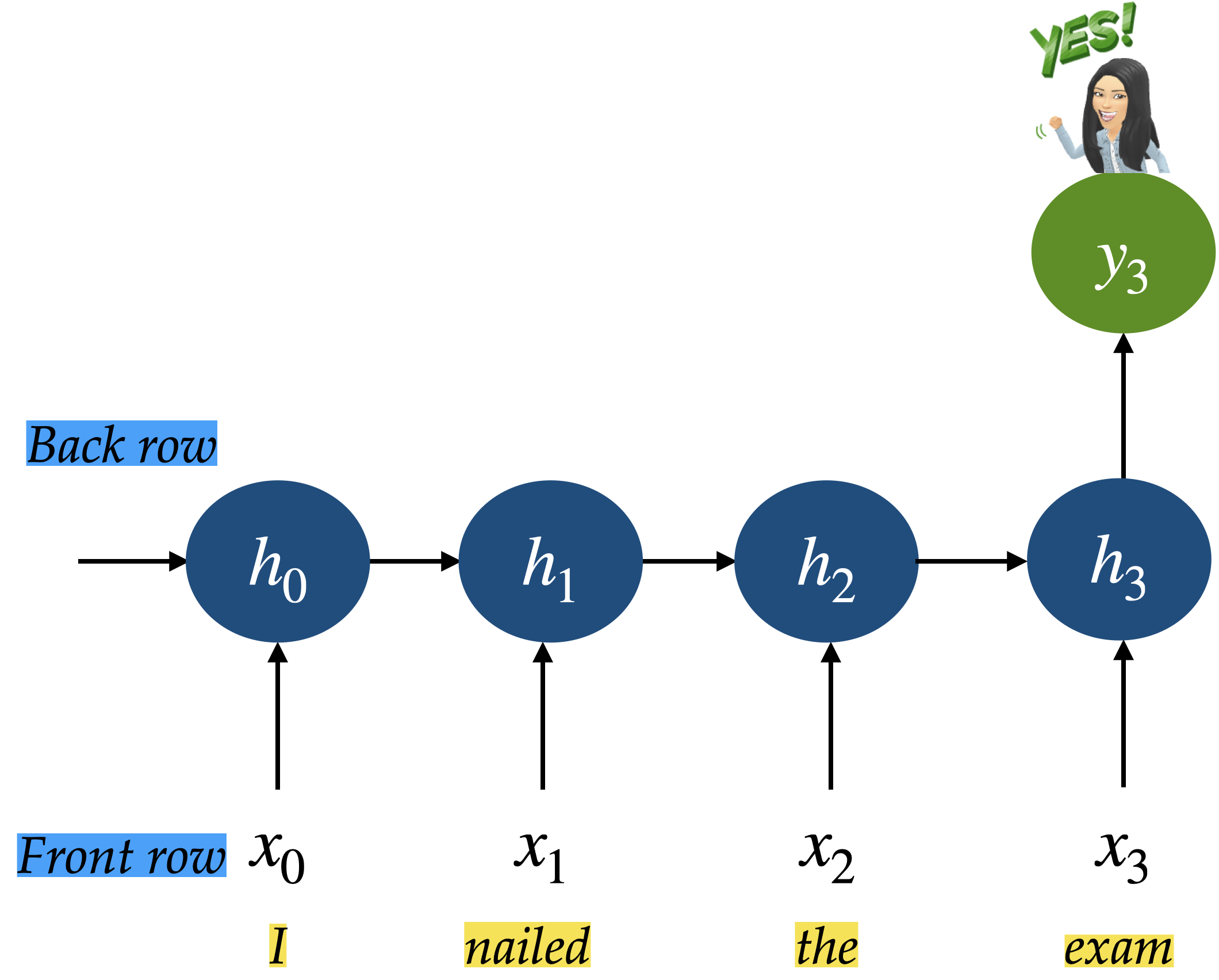
RNN
RNN is like your brain reading a sentence word by word.
Input at each time step: The current word you read
Hidden state: Your current mental understanding
Output: Your interpretation, reaction, or prediction at that point in time
Two rows of students:
Front row = input layer (observations at each time step)
Back row = hidden state at each time step
Each column is a time step (0 through 4)
So we’ll have 4 front-row students: to
And 4 back-row students: to
At time step 0:
Front-row student gets a word
They pass it to the back-row student behind them ().
is initialized with an image if you want to make it interesting
At time step 1 (and beyond):
The front-row student (e.g., ) gets a new word
The back-row student (e.g., ) receives:
The current input from the front-row student (e.g., )
Whatever “memory” is passed from the previous hidden state (e.g., )
combines this (e.g., by writing a summary phrase or combining keywords).
Repeat until time step 3 or 4.
Final time step: summarizes what they remember (e.g., predicts next word, gives the “mood” of the sentence, etc.)
Embodied Activity: Markov Models of Language¶
Each of you will receive a sticky note with a word on it. Here’s what you’ll do:
Carefully remove the sticky note to see the word. This word is for your eyes only; don’t show it to your neighbours!
Think quickly: what word would logically follow the word on the sticky note? Write this next word on a new sticky note. You have about 20 seconds for this step, so trust your instincts!
Pass your predicted word to the person next to you. Do not pass the word you received from your neighbour forward. Keep the chain going!
Stop after the last person in your row/table has finished.
Each row/table reads their generated sentence.
Whichever row generates the most captivating sentence will get XXX.
Here are some example sentences generated by students.
Row 1: We trust God is student study Hard Rock Johnson buys candy
Row 2: Is student study hard rock johnson buys candy
Row 3: Data center tendency increase fluctuation during afternoon tea party invitation acceptance
Row 4: The size of candy sweet pudding gross grossy yard fence (??????) 😀
Row 5: We play games are mingle cuddle pet cat licking ice cream with you eat.
Row 6: What are you talking about?
Row 7: I like to eat ramen spicy story time series in the game time off
Course Structure: Spiral Learning¶
The spiral learning approach is described in this paper, below is the abstract reproduced:
Introductory courses often present techniques in a linear sequence, resulting in a steep learning curve that can overwhelm students and limit the time for experiential learning through course projects. To address this, I restructured the course using a spiral approach, presenting concepts in three iterations. Each iteration delves deeper into the material and introduces complex computational topics progressively. This method includes a built-in repetition mechanism that reinforces learning and enhances understanding. Moreover, this approach allows time for hands-on projects that apply theory to real-world scenarios, helping students better understand the course materials. The spiral approach was implemented in an ML course at a local university, resulting in positive student feedback and improved course retention rates.
Traditional linear approach
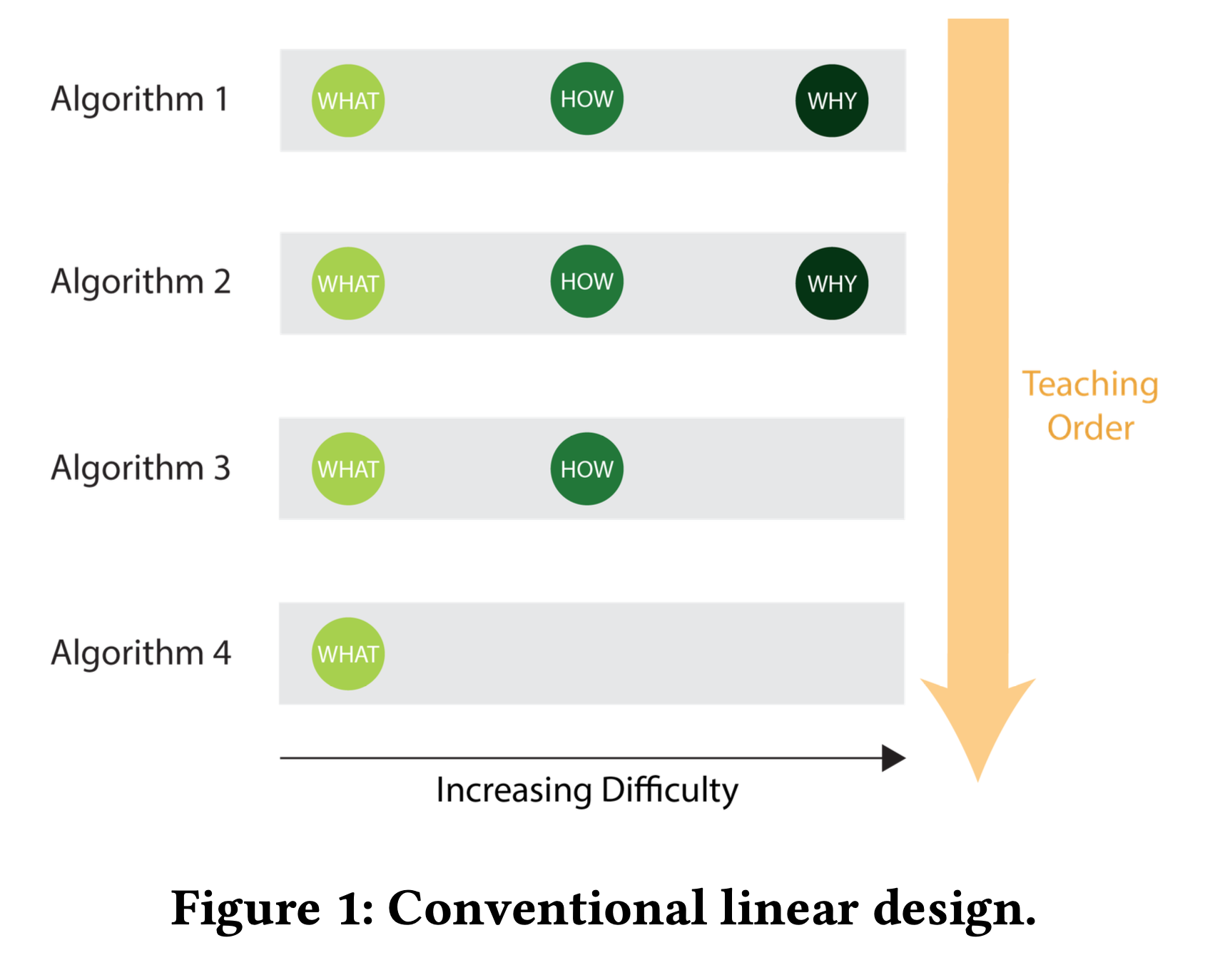
Linear approach to course design
Spiral learning approach
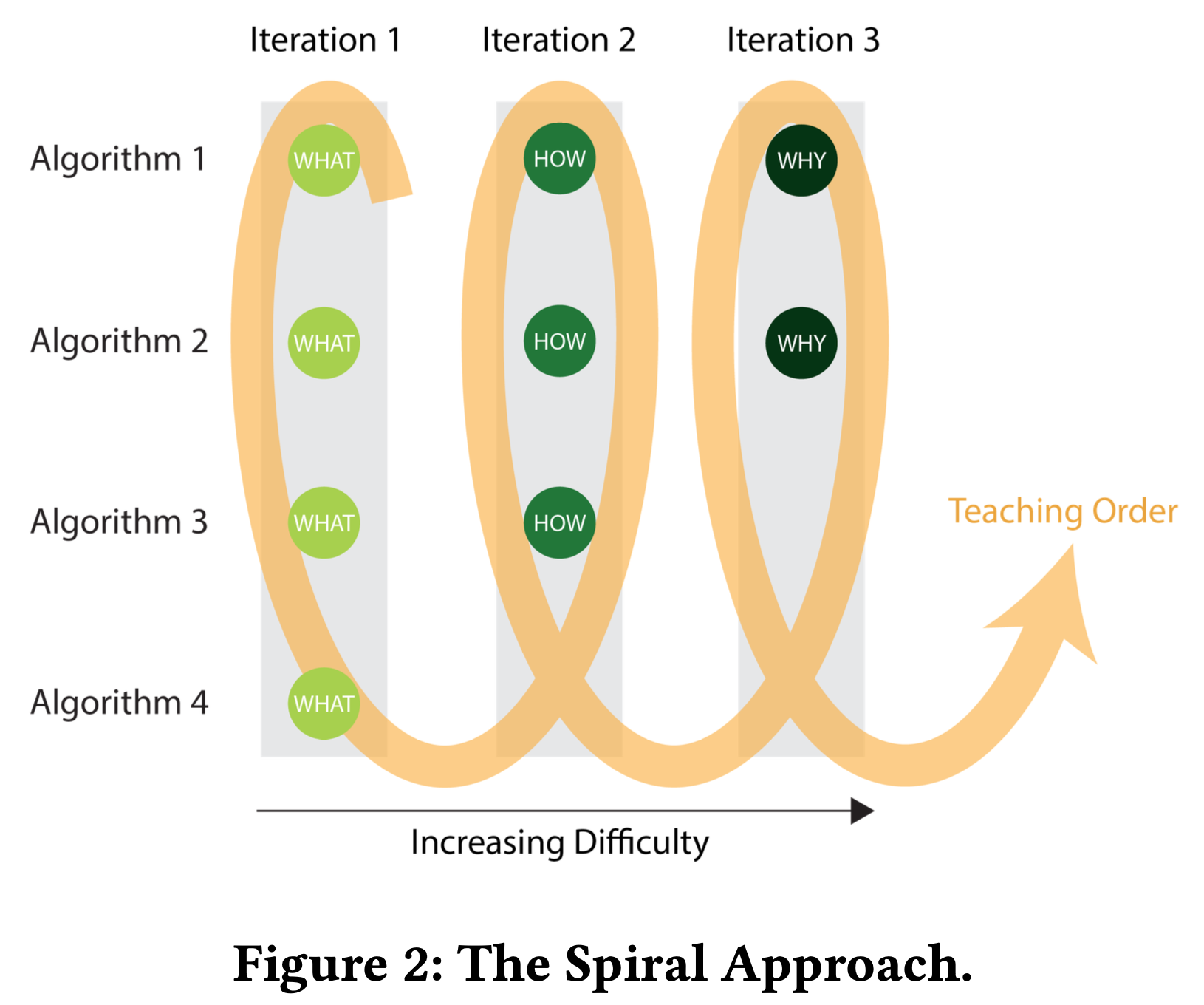
Spiral approach to course design
- Qin, M. (2025). Approachable Machine Learning Education: A Spiral Pedagogy Approach with Experiential Learning. Proceedings of the 56th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, 924–930. 10.1145/3641554.3701783